.gtr-container-def456 {
font-family: Verdana, Helvetica, "Times New Roman", Arial, sans-serif;
color: #333;
line-height: 1.6;
padding: 15px;
max-width: 100%;
box-sizing: border-box;
border: none !important;
}
.gtr-container-def456 * {
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.gtr-container-def456 .gtr-title-main {
font-size: 16px;
font-weight: bold;
margin-bottom: 15px;
color: #2c3e50;
text-align: left;
}
.gtr-container-def456 .gtr-title-sub {
font-size: 15px;
font-weight: bold;
margin-top: 20px;
margin-bottom: 10px;
color: #34495e;
text-align: left;
}
.gtr-container-def456 p {
font-size: 14px;
margin-top: 0;
margin-bottom: 10px;
text-align: left !important;
word-break: normal;
overflow-wrap: normal;
}
.gtr-container-def456 ol,
.gtr-container-def456 ul {
list-style: none !important;
margin: 0 !important;
padding: 0 !important;
margin-bottom: 15px !important;
}
.gtr-container-def456 li {
font-size: 14px;
margin-bottom: 8px;
padding-left: 25px;
position: relative;
text-align: left;
}
.gtr-container-def456 ol li::before {
content: counter(list-item) ".";
counter-increment: none;
position: absolute;
left: 0;
top: 0;
font-weight: bold;
color: #007bff;
width: 20px;
text-align: right;
}
.gtr-container-def456 ul li::before {
content: "•";
position: absolute;
left: 0;
top: 0;
font-weight: bold;
color: #007bff;
font-size: 18px;
line-height: 1;
}
.gtr-container-def456 .gtr-separator {
border-top: 1px solid #ddd;
margin: 30px 0;
}
.gtr-container-def456 .gtr-table-wrapper {
width: 100%;
overflow-x: auto;
margin-bottom: 15px;
}
.gtr-container-def456 table {
width: 100%;
border-collapse: collapse !important;
border-spacing: 0 !important;
margin-bottom: 15px;
font-size: 14px;
color: #333;
}
.gtr-container-def456 th,
.gtr-container-def456 td {
border: 1px solid #ccc !important;
padding: 8px 12px !important;
text-align: left !important;
vertical-align: top !important;
word-break: normal;
overflow-wrap: normal;
}
.gtr-container-def456 th {
font-weight: bold;
background-color: #f0f0f0;
color: #2c3e50;
}
.gtr-container-def456 tr:nth-child(even) {
background-color: #f9f9f9;
}
.gtr-container-def456 img {
max-width: 100%;
height: auto;
display: block;
margin: 0 auto 15px auto;
}
.gtr-container-def456 .gtr-image-group {
display: block;
margin-bottom: 15px;
}
.gtr-container-def456 video {
max-width: 100%;
height: auto;
display: block;
margin: 0 auto 15px auto;
}
@media (min-width: 768px) {
.gtr-container-def456 {
padding: 25px;
max-width: 800px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.gtr-container-def456 .gtr-title-main {
font-size: 18px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
.gtr-container-def456 .gtr-title-sub {
font-size: 16px;
margin-top: 25px;
margin-bottom: 12px;
}
.gtr-container-def456 p {
margin-bottom: 12px;
}
.gtr-container-def456 li {
margin-bottom: 10px;
}
.gtr-container-def456 .gtr-image-group {
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
gap: 15px;
}
.gtr-container-def456 .gtr-image-group .gtr-image-item {
flex: 1 1 calc(50% - 7.5px);
max-width: calc(50% - 7.5px);
}
}
チタンの主な利点(なぜチタンは航空宇宙で"愛される"のか?)
1. 優れた重量比(高強度、低密度): チタンの密度は約4.5 g/cm³で、これは鋼のわずか60%ですが、その強度は多くの高強度鋼に匹敵します。これは、同じ強度と剛性の要件に対して、チタン合金を使用すると、鋼と比較して大幅な軽量化が可能になることを意味します。軽量化は航空宇宙における永遠のテーマであり、 1キログラムの節約は、大幅な燃費向上、航続距離の延長、またはペイロード容量の増加につながります。
2. 優れた耐食性: チタンの表面には緻密で安定した酸化層(TiO₂)が形成され、大気、海水、および航空宇宙で一般的な化学物質(油圧作動油や除氷液など)に対する极高の耐性を付与します。その耐食性はステンレス鋼よりもはるかに優れています。これにより、コンポーネントの寿命と信頼性が大幅に向上し、メンテナンスコストが削減されます。
3. 優れた高温性能: 従来のチタン合金(Ti-6Al-4Vなど)は、400〜500℃で長期間安定して動作できますが、一部の特殊な高温チタン合金(Ti-Al金属間化合物など)は、600℃以上にも耐えることができます。これにより、航空機エンジンの高温部材に最適です。
4. 複合材料との適合性: チタンは、炭素繊維強化ポリマー(CFRP)複合材と類似した電気化学的腐食電位を持っています。両者が接触しても、深刻なガルバニック腐食を起こしません。したがって、チタンは、複合材部品に接続されたファスナー、ブラケット、および接合部に使用されることがよくあります。
主な用途分野
1. 航空機エンジン – チタンの最大の市場
エンジンは航空機の「心臓部」であり、チタン合金の最も使用量が多いコンポーネントです(エンジンの総重量の約25%〜40%を占めます)。
ファンブレード: 最新の高推力ターボファンエンジン(LEAP、GEnxなど)のフロントファンブレードには、一般的にチタン合金が使用されています。これらは、巨大な遠心力と異物衝突に耐えるために、非常に高い強度を必要とします。
コンプレッサーディスクとブレード: コンプレッサーの低圧段のディスク、ブレード、ケーシングには、チタン合金が広く使用されています。これらのコンポーネントは、高温、高圧環境で動作し、高強度、耐疲労性、および耐クリープ性を備えた材料を必要とします。
エンジンナセルとストラット: これらの構造コンポーネントも、軽量化のためにかなりの量のチタン合金を使用しています。
2. 機体構造
航空機の機体では、チタン合金は、従来のアルミニウム合金では要件を満たすことができない領域を中心に、重要な荷重支持構造に使用されています。
着陸装置コンポーネント: 着陸装置は、着陸時の巨大な衝撃力と静的荷重に耐えなければならず、航空機で最も負荷の高いコンポーネントの1つです。高強度チタン合金(Ti-10V-2Fe-3Alなど)は、重要な着陸装置ビーム、ストラット、およびトルクリンクの製造に使用されます。
翼と胴体の接合部: 翼と胴体を接続するセンターウィングボックス、フラップトラック、キールビームなどの重要な荷重支持コンポーネントには、集中荷重のため、高強度チタン合金鍛造品がよく使用されます。
ファスナー: チタン合金のリベット、ボルト、ネジ、その他のファスナーは、強度が高く、軽量で、耐食性があるため、広く使用されています。
油圧システムとパイプライン: チタンの優れた耐食性により、複雑な油圧パイプラインシステムの製造によく使用され、長期的な信頼性を確保しています。
3. 宇宙船
宇宙分野では、軽量化の利点はさらに重要であり(打ち上げ能力に直接関連)、極端な温度環境と宇宙の真空に耐える必要性も重要です。
ロケットエンジン: 液体燃料ロケットエンジンのコンポーネント(推進剤タンク、ターボポンプ、インジェクターなど)は、低温液体酸素/水素の腐食と高圧に耐えるためにチタン合金を使用しています。
圧力容器: 高圧ガス(ヘリウムなど)と推進剤の貯蔵に使用されるチタン合金ガスシリンダーは、軽量で、高い耐圧性を持ち、優れた信頼性を提供します。
衛星構造: 衛星ブラケット、接続フレーム、カメラミラーバレル、その他の構造コンポーネントは、宇宙環境における構造的安定性、軽量設計、および高剛性の厳しい要件を満たすためにチタン合金を使用しています。
有人宇宙船: 神舟やソユーズなどの有人宇宙船は、帰還モジュールの荷重支持構造にチタン合金を広く使用しています。
チタンは主に以下の分野で使用されます.
1整形インプラントこれはチタンで最も広く 確立された用途です
人工関節:ヒップ関節,膝関節,肩関節,肘関節など. 重要な負荷を負担する構成要素である大腿幹や足首のカップは主にチタン合金で作られています.
トラウマ修復骨 の プレート,螺栓,内膜 釘 を 用い,骨折 を 固定 する.これら の 装置 は,骨折 を 安定 さ せ,骨 の 治癒 を 促進 する.
脊髄融合体間融合装置,チタン網,骨頭螺旋システム 脊椎骨折矯正と椎間板置換手術に使用される.
2歯科インプラントと義肢
歯科インプラント歯科 の "金 の 標準"である タイタン 植入物 は,人工 根 の よう に 歯骨 に 埋め込まれて 強い 歯根 を 形成 し ます.骨統合骨に冠が付けられ
歯の入れ替えの枠組み脱ぎ取れる義歯用の金属フレームや 冠や橋のベースは 軽さや耐久性,アレルギー発生性の低さにより タイタンを使用することが多い.
矯正歯科機器:矯正歯科 の 矯正歯科 の 支架 や 弓線 も チタン 合金 で 作ら れ ます.
3心血管介入器具
ペースメーカーとデフィブリレータータイタンのカビは優れた密封性を提供し,内部精密な電子部品を保護し,同時にヒト組織と生物互換性があり,拒絶反応を軽減します.
血管ステント:コバルト・クロム合金と生物分解可能な材料が現在主流であるにもかかわらず,ニッケル・チタン合金 (ニチノール) は,独特の特性により,自己拡張血管ステントに使用されています.超弾力性そして形状記憶効果特に大動脈や下肢動脈のような部位です
4手術器具と設備
手術用器具:タイタンのピンプ,シザ,リラクターなど,不?? 鋼機器よりも軽く,疲労耐性が高く,腐食耐性があります.繰り返し高温消毒に耐える.
医療機器の部品:MRI スキャナー,ロボット 手術用腕など 内部部品磁性でない性質MRI環境での安全性にとって極めて重要であり,画像の干渉を避ける.
5顔と頭蓋骨の再構築
トラウマ や 手術 に よっ て 引き起こ さ れ た 頭蓋骨 や 顔 の 骨 の 欠陥 を 修復 する ため に 用い られ て いる タイタン の メッシュ や プレート.その 形 は 機能 や 外見 を 回復 する よう に 精密 に 形作れ ます.
2チタン材料の主要な利点
医療分野におけるチタンの代替不可能な役割は,その例外的な特性から生じます.
1優れた生物互換性表面は自然に密集し安定したチタン酸化物被動膜を形成し,化学的に惰性であり,ヒト組織や液体と反応することはめったにありません.炎症を予防しますアレルギーや排斥反応を 引き起こします直接的な結合と機能的な結合生きた骨組織で骨統合インプラントの長期安定性にとって重要です.
2高強度重量比と低弾性モジュール
高強度/重量比:タイタンの強さは多くの鋼に匹敵するが,密度は (~4.5g/cm3) 鋼の約60%に過ぎず,インプラントを軽くし,患者の負担を軽減する.
低弾力モジュールタイタンの弾力積 (~110 GPa) は,人間の骨 (10-30 GPa) に近いが,不?? 鋼やコバルト・クロム合金よりもはるかに低い.ストレスの遮断効果硬いインプラントがストレスの多くを 負うため 周囲の骨が 毛穴になり 機械的な刺激がないため 吸収されますタイタンインプラントにより 骨に自然に ストレスが 伝わります癒しと長期的な安定を促進します
3優れた耐腐食性体液は,塩化物イオン (例えば,塩化塩化物) を含む腐食性環境である.チタンの受動性フィルムは,生理環境で非常に高い腐食耐性を有します.腐食に耐えるようにするこれは,次のとおりです.
長いインプラント寿命腐食による故障はありません
生物互換性が高い組織毒性や金属イオン放出によるアレルギー反応 (ニッケルアレルギーなど) を避ける.
4磁性でない性質タイタン 植入 器 を 持つ 患者 たち に 安全 に 治療 を 施す こと が でき ますMRI スキャン手術後の診断と監視に不可欠な インプラントの加熱や 移転や画像処理の干渉を心配することなく
5機械加工と形容性の良さ純粋なチタンは柔らかいものの,合金 (例えば,Ti-6Al-4V を形成するアルミとバナジウム) と先進的な加工技術により,個別の外科手術ニーズを満たす複雑な形状のインプラントの生産が可能になります.形状記憶効果ニッケル・チタン合金で 独自のソリューションを 提供しています
概要 と 将来 展望
資産
利点
応用例
生物互換性
毒性がない,アレルギー発生しない,骨組み合体
すべてのインプラントの長期的安全性
メカニカルプロパティ
軽量で強度が高い ストレスの遮蔽が低かった
骨 を 保護 し て いる とき に,関節,脊椎,骨板 の 優れた 負荷 負ける 能力
耐腐食性
寿命が長い 離子排出量が少ない
長期安定性と体内の高い安全性
磁性でない性質
MRIスキャンには安全です
手術後の画像追跡を容易にする
処理可能性
複雑な形に形作れる
パーソナライズされたインプラントと最小侵襲性手術器具
将来の傾向:
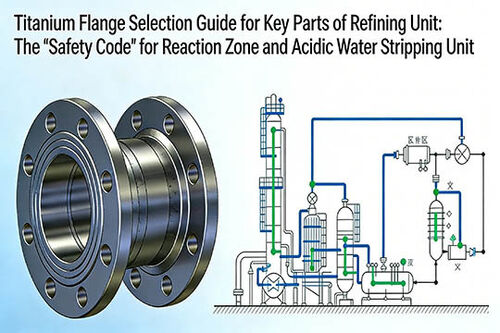
要約すると、優れた耐食性、高強度、長寿命、そして卓越した環境への優しさから、チタンフランジは、腐食性媒体を扱い、長期的な設備安定性が求められる環境工学プロジェクトにおいて、特に重要なコンポーネントとなっています。I. 環境保護におけるチタンフランジの具体的な用途チタンフランジは、パイプ、バルブ、および機器を接続し、システムのシール性と構造的完全性を確保するために使用される配管システムにおける不可欠な接続部品であり、環境分野における以下の高度に腐食性の高い環境で主に利用されています。
排煙脱硫(FGD)システム
適用シナリオ:
火力発電所、廃棄物焼却プラント、および冶金/化学産業におけるテールガス処理システム。これらの排ガスには大量の
役割:、塩化物(例:HCl)、フッ化物、および水分が含まれており、高度に腐食性の酸性環境(例:希硫酸、亜硫酸)を作り出します。役割: チタンフランジは、FGDシステム内の吸収塔、ダクト、スプレーシステム、および再循環配管を接続するために使用されます。これらは、腐食性ガス処理システム全体が漏れなく維持されることを保証する重要な接続点です。
II. チタンフランジの主な利点適用シナリオ:
化学、製薬、電気メッキ、印刷、染色、および製紙産業からの高濃度排水の処理プラント。この排水にはしばしば
役割:、強酸(例:塩酸、硫酸)、強アルカリ、酸化性化学物質などが含まれています。役割: チタンフランジは、反応釜、沈殿槽、ろ過ユニット、高度酸化(例:オゾン処理)パイプライン、および排水搬送パイプを接続します。特に、塩化物による応力腐食割れ(SCC)に対する耐性が求められる領域で使用されます。
II. チタンフランジの主な利点適用シナリオ:
逆浸透(SWRO)および多段フラッシュ蒸留(MED)を使用する海水淡水化プラント。海水は、塩化物イオンを高濃度で含む自然な強電解質であり、ほとんどの金属に対して非常に腐食性が高いです。
役割: チタンフランジは、海水取水管、前処理システム、高圧逆浸透膜ハウジングの接続、および蒸留ユニットの熱交換システムの接続部分に広く使用されています。
II. チタンフランジの主な利点適用シナリオ:
酸、アルカリ、または有機溶剤を含む有害廃棄物液体の処理施設。
役割: これらの非常に有害な媒体の輸送および処理中に、パイプライン接続点における絶対的な安全性と信頼性を確保し、有害物質の漏洩を防ぎます。
II. チタンフランジの主な利点適用シナリオ:
より工業的ではありますが、その環境的なエンドオブパイプ処理は密接に関連しています。塩素、塩酸、王水などを含むプロセスで、反応と抽出に使用されます。
役割: 機器と配管間の接続に使用され、生産およびリサイクルプロセスの封じ込めを保証します。
II. チタンフランジの主な利点チタン(特にGR2、GR1などの市販の純粋グレード)は、環境用途において、ステンレス鋼(例:304、316L)、二相鋼、およびニッケル基合金(例:ハステロイ)などの他の材料と比較して、かけがえのない利点を提供します。
優れた耐食性(主な利点)
塩化物イオン腐食に対する耐性:
これはチタンの最も顕著な利点です。チタンは
孔食 および 応力腐食割れ(SCC) に対して本質的な免疫力を持っています。これは、ステンレス鋼が非常に脆弱であるのに対し、チタンは非常に長い耐用年数を持ちます。これは、海水、塩化物を含む排水、および排ガス(HClを含む)を扱う場合に非常に長い耐用年数を与えます。酸性環境に対する耐性: チタンは、酸化性酸(例:硝酸、クロム酸)および弱い還元性酸において良好な性能を発揮します。非酸化性酸(例:純粋な塩酸、硫酸)では腐食が速くなりますが、FGD環境では、酸化剤(例:SO₂、O₂)の存在により、表面に
緻密で安定した酸化チタン(TiO₂)不動態皮膜 が急速に形成され、さらなる腐食を効果的に阻止します。隙間腐食に対する耐性: フランジ接続は隙間腐食を起こしやすいです。高塩化物環境におけるチタンの隙間腐食に対する耐性は、ステンレス鋼よりもはるかに優れています。
優れた機械的強度と軽量性チタンは高強度ですが、密度(〜4.51 g/cm³)は鋼(〜7.9 g/cm³)よりもはるかに低いです。これは、同じ強度要件の場合、チタンフランジをより軽量にできることを意味し、
システム負荷を軽減
するのに役立ちます。これは、大型の吸収塔や高架ダクトにとって特に有利です。長寿命と低いライフサイクルコスト(LCC)チタンの初期材料コストはステンレス鋼よりも高いですが、その事実上メンテナンスフリーな性質、非常に低い故障率、および超長の耐用年数(20〜30年以上、ステンレス鋼は数年で交換が必要になる可能性があります)は、
総所有コスト
を大幅に削減します。これは、交換と修理のためのダウンタイムによって引き起こされる大規模な生産損失と二次的な投資を回避し、長期的には非常に経済的です。優れた環境への優しさと安全性
生体適合性:
チタンは無毒で無害であり、人体組織および環境との適合性が良好です。腐食生成物がシステムに入っても、二次的な汚染を引き起こさないため、排出物の品質が重要な水処理に非常に適しています。
高い安全性: その高い信頼性により、腐食によるパイプラインの故障や有害物質の漏洩のリスクが大幅に軽減され、環境とオペレーターの安全を保護するために不可欠です。
良好な製造特性チタンフランジは、鍛造、鋳造などによって製造でき、さまざまな圧力定格(PN6-PN100)および規格(GB、ASME、JISなど)に対応しています。
III. 他の材料との比較
特性
チタン(GR2)
316Lステンレス鋼
二相鋼2205
ハステロイC-276
Cl⁻耐食性
優れている
悪い(孔食/SCCを起こしやすい)
高い
優れている
初期コスト
高い
低い
低い/軽い
中程度
低い
高い(頻繁な交換)
中程度
高い
低い/軽い
高い/重い
高い/重い
適用可能なpH範囲
適用可能なpH範囲
広い
狭い
中程度
化学産業における具体的な用途
チタン材料は、主に腐食性の高い媒体を扱うほぼすべての化学サブセクターで使用されており、主に の形で使用されています。反応器、圧力容器、熱交換器、塔、パイプライン、継手、バルブ、ポンプ、アジテーター、電極。
以下に典型的な用途シナリオをいくつか示します。
1. 苛性ソーダ産業(最大の化学用途)
苛性ソーダ産業は、苛性ソーダ、塩素、水素を生産しており、これらはすべて腐食性の高い媒体です。
用途別機器:
イオン膜電解槽: チタンは、アノード室(塩素、塩酸、次亜塩素酸に曝露)、アノードプレート、冷却パイプのコア材料として使用されています。これは、化学産業におけるチタンの最大の用途です。
湿式塩素ガス冷却器/熱交換器: チタンの耐食性により、高温湿式塩素ガス用のシェルアンドチューブまたはプレート型冷却器を製造するための唯一の経済的に実行可能な金属材料となっています。
塩素ガススクラバー、乾燥塔、および供給パイプライン: チタンは、湿式および乾式塩素ガスを扱うシステム全体で広く使用されています。
2. ソーダ灰(炭酸ナトリウム)産業
用途別機器:
外部冷却器、コンデンサー、および冷却器: ソーダ灰の製造プロセスでは、媒体には高濃度の塩化物イオン(Cl⁻)とアンモニウムイオン(NH₄⁺)が含まれており、ステンレス鋼に深刻な孔食と応力腐食を引き起こします。チタン熱交換器は、この問題を完全に解決し、ステンレス鋼製の機器の1〜2年と比較して、20年以上の耐用年数があります。
3. 尿素産業
用途別機器:
尿素合成塔、高圧熱交換器、およびストリッピング塔: 尿素の製造は高温高圧下で行われ、中間生成物であるカルバミン酸アンモニウムは非常に腐食性が高いです。初期のステンレス鋼の使用には酸素不動態化保護が必要であり、耐用年数は限られていました。チタンライニングまたはオールチタン製の機器を採用することで、耐用年数が大幅に延長され、安全性と信頼性が向上します。
4. 硝酸産業
用途別機器:
硝酸リボイラー、コンデンサー、加熱コイル、ポンプ、およびバルブ: チタンは、さまざまな濃度と温度の硝酸(発煙硝酸を除く)において優れた安定性を示し、ステンレス鋼やアルミニウム合金よりも優れた耐食性を備えています。
5. 有機およびファインケミカル
用途別機器:
反応ケトル(ジャケットまたはコイル付き)およびコイル: 農薬、染料、医薬品中間体、化粧品(例:酢酸環境)などの製造に使用されます。塩化物、塩酸、有機酸などの腐食性媒体が関与する場合、チタン製の機器は純粋な反応環境を提供し、製品への金属イオン汚染を回避します。
PTA(精製テレフタル酸)製造: チタンは、酢酸媒体中の反応器と熱交換器を製造するための主要な材料です。
6. 海水冷却と脱塩
用途別機器:
発電所および化学プラント用海水冷却器: チタン管熱交換器は、海水浸食および腐食に対する比類のない耐性があるため、沿岸発電所および化学プラントの標準的な設備です。
海水脱塩プラント: 多段フラッシュ(MSF)または低温多効果(MED)脱塩プラントの熱伝達管は、長期的な安定した水生産率を確保するために、ほぼ独占的にチタン管を使用しています。
3D プリント に おける チタン の 主要 な 利点
3Dプリンタ技術では 伝統的なチタン合金加工における 多くの問題に対処し その利点を最大化します
伝統的な製造の課題を克服し",フリーフォーム製造"を可能にします
利点:伝統的にチタン部品は,鍛造と加工 (CNC) に大きく依存しており,その結果,材料の利用量は非常に低く,コストは高く,そして長期間3Dプリンティングは網に近い形高価な高性能材料に最適です 材料の廃棄物もほとんど発生せず 最小限の後処理が必要になります
利点:伝統的な製造の制約を破り,非常に複雑な内腔,不規則な管,単体構造減算方法では不可能です
デザイン の 大いなる 自由 と 軽量 化 の 可能性
利点:組み合わせるとトポロジーの最適化そして格子構造3Dプリンタでは 非常に軽量で優れた機械性能を持つ部品が作れます固い内部を堅牢な網状構造に置き換えることで,強さを維持しながら体重を大幅に減らすことができます航空宇宙産業の"グラムシェービング"哲学にとって 極めて重要です
低容量,カスタマイズされた生産のためのコストメリット
利点:伝統的な鋳造や鍛造には 高価な模具と固定装置が必要で,大量生産にのみ適しています.模具は必要ないデジタルファイルは直接生産を動かすことができます.それは特に低容量,カスタマイズされた製品 (例えば,医療インプラント,衛星部品,プロトタイプ) に適しています.単位コストがほとんど変わっていない場合.
材料 の 優れた 特性 と 密度
利点:チタン印刷の主要な技術とは選択レーザー溶融 (SLM)そして電子ビーム・メルト (EBM)この技術では,高エネルギー源を用いて金属粉末を層ごとに完全に溶解し,融合させ,生成された部品は990.7%機械的特性 (強度,疲労耐性)伝統的な鋳造を上回る偽造物と同じです
機能的統合と簡素化された生産
利点:複雑な組成物は,元々複数の部品から構成され,単一の部品で整体印刷これは,組み立て要件を削減し,潜在的な弱点 (例えば,溶接,ニット) を排除し,製品の全体的な信頼性と性能を改善します.
概要 比較
特徴
伝統的な加工 (鍛造/CNC)
3Dプリンティング (添加製造)
物質 の 利用
低 (廃棄物の5%~10%が一般的です)
非常に高い (ほぼ100%)
デザイン の 複雑さ
限定
ほぼ 無 制限 の 自由
生産 リード タイム
長さ (道具/固定装置が必要)
短編 (デジタルファイルから直接)
パーソナライゼーションコスト
非常に高い
比較的低い
適したバッチサイズ
大量生産
低音量 パーソナル化
統合 的 な 形成
難しい 組み立てが必要
簡単で 1 枚で印刷できます
結論として 3Dプリンタ技術により タイタンは "加工が難しい高性能材料"から "極端なデザインを実現できるスマートな材料"に変わりました" 製造方法だけでなく デザイン哲学にも 大きな飛躍をもたらした "高技術分野におけるチタン合金の使用範囲を大幅に拡大する.
高強度チタン合金ロッドは、優れた重量比強度、優れた耐食性、および極限条件下での性能で知られる重要なエンジニアリング材料です。これらの特性により、軽量で耐久性があり、信頼性が最重要視される幅広い業界で不可欠な存在となっています。以下に、高強度チタン合金ロッドの主な用途を詳しく見ていきます。
1. 航空宇宙産業
航空宇宙部門は、高強度チタン合金ロッドの最大の消費者です。これらのロッドは、次のような重要なコンポーネントの製造に使用されています。
エンジン部品: Ti-6Al-4V (グレード5) などのチタン合金は、コンプレッサーブレード、ファンディスク、ローターシャフトなど、ジェットエンジン部品に使用されています。高い強度と耐熱性 (最大600℃) により、要求の厳しい環境での効率と安全性が確保されます。
機体構造: チタンロッドは、着陸装置、翼支持、ファスナーに使用されており、構造的完全性を維持しながら重量を削減します。この軽量化は、燃費の向上とペイロード容量の向上につながります。
宇宙船とミサイル: 極端な温度と腐食に対する耐性により、チタン合金はロケットモーターケーシング、衛星コンポーネント、ミサイルボディに最適です。
2. 医療とヘルスケア
チタンの生体適合性と体液に対する耐性により、医療機器に最適な材料となっています。
整形外科用インプラント: Ti-6Al-4V ELI (Extra Low Interstitial) などの合金で作られたロッドは、脊椎固定デバイス、骨プレート、関節置換に使用されています。その強度と柔軟性は天然の骨を模倣し、より速い治癒を促進します。
外科用器具: チタンロッドは、腐食することなく繰り返し滅菌に耐える軽量で耐久性のあるツールに加工されています。
歯科インプラント: その無毒性および骨結合特性により、歯科用途での長期的な安定性が確保されます。
3. 海洋およびオフショアエンジニアリング
海洋環境の腐食性は、優れた耐性を持つ材料を必要とします。
造船: チタンロッドは、プロペラシャフト、熱交換器、潜水艦船体に利用され、メンテナンスコストを削減し、耐用年数を延長します。
オフショア石油およびガス: 掘削ライザーやバルブシステムなどのコンポーネントは、海水や酸性ガス (H₂S) 腐食に対するチタンの耐性の恩恵を受けています。
4. 化学およびプロセス産業
チタン合金は、腐食性の強い化学物質や高温に耐えます。
反応器と熱交換器: ロッドは、塩化物、酸、その他の腐食性物質を扱う機器の構築に使用されています。
配管とバルブ: チタンの耐久性により、化学処理プラントでの漏れのない性能が保証されます。
5. 自動車およびモータースポーツ
高性能車は、チタンの軽量強度を活用しています。
エンジン部品: コネクティングロッド、バルブ、排気システムは重量を削減し、速度と燃費を向上させます。
レーシングカーと高級車: チタンロッドは、ハンドリングと耐久性を向上させるために、サスペンションシステムとシャーシ補強に使用されています。
6. スポーツおよび消費者向け製品
スポーツ用品: ゴルフクラブシャフト、自転車フレーム、登山ギアには、軽量強度と耐衝撃性のためにチタンロッドが使用されています。
ハイエンドエレクトロニクス: ラップトップやカメラなどのデバイスでは、チタンロッドがバルクを追加することなく構造的なサポートを提供します。
7. エネルギー部門
原子力: チタン合金は、放射線耐性と高温での安定性により、熱交換器と冷却システムに使用されています。
再生可能エネルギー: 風力タービンコンポーネントと水素貯蔵システムは、チタンの耐食性と耐久性の恩恵を受けています。
8. 防衛と軍事
装甲車: チタンロッドは、重量を削減しながら装甲保護を強化します。
銃器と大砲: 軽量で耐久性のあるコンポーネントは、機動性と性能を向上させます。
結論
高強度チタン合金ロッドは、業界全体でイノベーションを推進する多用途な材料です。その軽量性、強度、耐食性のユニークな組み合わせにより、失敗が許されない用途に最適です。技術が進歩するにつれて、これらのロッドの需要は、積層造形や再生可能エネルギーなどの新しい分野で特に増加すると予想されます。
管フィッティングの材料としてチタンは安定した化学特性と優れた生物互換性を表し,高耐腐蝕性と安定性を持っています.人体に有害な効果がないしアレルギー反応を引き起こさない金属になります.
チタン管フィッティングの特徴は,主に以下の側面に反映される.
耐腐食性タイタンの管材は,特殊な耐腐蝕性を持っています.湿気や海水にさらされたときでさえ,その耐腐蝕性は,不oxidable steelよりもはるかに優れています.耐腐蝕性15倍,使用寿命約10倍.
低温 に 耐えるチタン管フィッティングは低温でも機械的性能を維持し,冷たい環境に強い耐性がある.
高強度チタン合金の密度は通常4.51g/cm3程度で,鉄鋼の密度は60%に過ぎません.このにもかかわらず,チタン管フィッティングは非常に高い強度を示しています.他の金属構造材料の性能をはるかに上回る.
高熱強度タイタン管フィッティングは,熱強度が優れ,温度450~500°Cに長期にわたって曝されても安定性を維持しています.チタン合金 500°Cまで温度で動作するアルミニウム合金では通常200°Cに制限されます.
滑らか な 表面 と 汚れ を 防げる 特性低密度で軽量なチタンは 滑らかな表面を備えています日常用途におけるチタン管フィッティングの使用により,スケーリング係数が大幅に減少します.
これらの5つの主要特性のおかげで,チタン管フィッティングは,化学機器,海上発電施設,海水淡化システム,船舶部品そして電圧加工業界です
.gtr-container-f7d9e2 {
font-family: Verdana, Helvetica, "Times New Roman", Arial, sans-serif;
color: #333;
line-height: 1.6;
padding: 16px;
max-width: 960px;
margin: 0 auto;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.gtr-container-f7d9e2 .gtr-intro-statement {
font-size: 18px;
font-weight: bold;
margin-bottom: 24px;
color: #0056b3;
text-align: left !important;
}
.gtr-container-f7d9e2 .gtr-section-title {
font-size: 18px;
font-weight: bold;
margin-top: 32px;
margin-bottom: 16px;
color: #2c3e50;
text-align: left !important;
}
.gtr-container-f7d9e2 p {
font-size: 14px;
margin-bottom: 16px;
text-align: left !important;
}
.gtr-container-f7d9e2 ol {
list-style: none !important;
margin: 0 0 16px 0 !important;
padding: 0 !important;
}
.gtr-container-f7d9e2 ol li {
position: relative;
padding-left: 30px;
margin-bottom: 12px;
font-size: 14px;
text-align: left !important;
}
.gtr-container-f7d9e2 ol li::before {
content: counter(list-item) ".";
counter-increment: none;
position: absolute;
left: 0;
top: 0;
font-weight: bold;
color: #0056b3;
width: 20px;
text-align: right;
}
.gtr-container-f7d9e2 ol li p {
margin: 0;
text-align: left !important;
}
.gtr-container-f7d9e2 strong {
font-weight: bold;
}
@media (min-width: 768px) {
.gtr-container-f7d9e2 {
padding: 24px 40px;
}
}
伝統的な鉄鋼の代わりに タイタンの室内体は 優れた生物互換性 優れた耐腐蝕性 軽量性があります患者と医療従事者の体験に革命をもたらします
先進的なチタンプレートから作られた 医療用大型の高圧酸素室グループが中国でトップクラスの病院で 臨床使用を開始しました首都医学大学に所属する北京天安病院,上海大学医学部に所属するルイジン病院を含む.中国人民解放軍総合病院 (301病院). The deployment of these high-end medical facilities has not only significantly increased the overall capacity and efficiency of hyperbaric oxygen therapy but has also earned high praise from both medical professionals and patients for their exceptional safety and unprecedented comfortこれは,チタン技術の採用によって特徴づけられる,中国の高圧酸素医療インフラストラクチャの新しい時代を意味します.
1伝統 を 覆す 材料 革命
伝統的な高圧酸素室は主に鋼製で作られています.この技術は成熟していますが,固有の欠点があります.重量,設置基盤の高い要求,長期にわたる高酸素で酸化や腐食に敏感である高湿度な環境です.これは高い保守コストと潜在的な安全リスクにつながります.強い金属の熱伝導性により,内部温度は外部条件によって容易に影響を受けます.快適さを減らします
提タン金属の導入は,これらの問題を完璧に解決します.
究極 の 安全 と 耐久 性:チタンは,非常に反応性のある金属ですが,その表面はすぐに密度が高い安定したチタン酸化物被動膜を形成します.このフィルムはチタンプレートを与えます.類を見ない耐腐蝕性高濃度の酸素,高湿度,および高圧酸素室内の消毒剤の侵食に完全に耐えるようにする.これは,腐食による強度低下による安全リスクを根本的に排除します設計寿命は,鉄鋼の室よりもはるかに長くなっています.高強度,低密度また,安全性を確保しながら,室内ボディを軽くする.
優れた生物 互換性 と 快適性:チタン は"生物 に 優しい 金属"として知られており,人工 関節 や 心弁 の よう な 植入物 に 広く 用い られ て い ます.室内 製造 に 用いる タイタン は 有害 な 物質 が 放出 さ れる こと を 保証 し ますさらに,チタンの低熱伝導性は,室内の"凝縮"を効果的に軽減します.壁の乾燥と安定した内部温度を維持するこれは,長時間治療中に患者の快適さを大幅に向上させ,窒息や湿度などの不快さを軽減します.
現代 美学 と 人性 的 な デザイン: チタンプレートは,追加的なコーティングを必要としない現代的な銀灰色の外観を持っています.快適な航空型座席統合された娯楽システムとインテリジェントな環境制御システムにより 患者には明るく広々とした快適な治療環境が提供されますクラウストロフォビーを効果的に緩和する.
2クリニカルフィードバック:医療従事者と患者の賛辞
北京天安病院の高圧酸素室で 治療を終えたばかりの 王氏は こう言いました "以前は 旧式の部屋とは 全く違う感じです窒息するわけじゃない とても乾燥し快適だテレビを見ると時間が早く過ぎ,リラックスさえする"
"チタン室のグループを採用することは,私たちの部門にとって質的な飛躍です. まず第一に,安全性室内の腐食を心配しなくなり,日々のメンテナンスの作業量は大幅に減少します.効率性大型の室内群は同時により多くの患者を治療することができ,最適化された治療環境は患者の従順性を著しく改善します.長期治療を必要とする神経リハビリ患者にとって重要です医療サービスの質を向上させるための 病院の努力の重要な部分でもあります"
3グローバルステージで中国製医療機器を代表する
最近使用開始されたチタン型高圧酸素室は,国内トップの圧力容器メーカーと医療機器会社によって独立して開発・製造されました.これは中国が世界レベルの高度な技術レベルを達成したことを充分に証明しています高級チタン加工(例えば大面積チタンプレート溶接技術や精密型成形技術など)専門医療機器の設計.
以前はハイエンド型高圧酸素室市場が 長い間 少数外国ブランドが支配していた.国内製チタン室の成功した応用は,輸入代替を達成し,医療機関のための調達コストを削減するだけでなく,優れた性能により,強力な国際競争力を形成し,すでに海外の顧客から注目を集めている.
結論は
The widespread application of titanium hyperbaric oxygen chamber groups is a classic case of new material technology innovation driving medical equipment upgrades and ultimately benefiting public welfare単なる材料の交換ではなく,より高い安全基準とより良いサービス体験を追求する患者中心の医療哲学を反映しています"第14五年計画"の進展により 国家医療センターと地域医療センターの建設将来,より多くの病院がこのような先進的な設備を導入し,より幅広い患者に世界クラスの高圧酸素療法サービスを提供すると予想されています.
タイタン (Ti) は,その強固な性質と幅広い用途で知られており,地球殻で9番目に豊富で,金属元素の中で4番目に多い元素です."Ti"で表記され,周期表で第22位で原子重量は47.90タイタンは,主にオーストラリアと南アフリカで採掘されるビーチ砂に含まれるルチールとイルメニットから得られます.
生産プロセスは,チタン四塩化物 (TiCl4) を出すために加熱されたコックスまたはタールおよび塩素ガスと組み合わせたルチールから始まります.この化合物は 化学 的 な 変換 を 受け て,スポンジ の よう な 物質 に なり ます合金品種には,圧縮中に合金剤を加えられる.製造された円筒印章は,標準的な金属加工機器を用いて,様々な工場製品に加工されます..
タイタンのメタルジカル特性により 航空宇宙,防衛,産業,化学加工,医療,海洋産業初期には,優れた構造的特性と強度対密度比のために軍事航空宇宙に不可欠であり,チタンの密度は0.160lb/in3から0です..175lb/in3,グレードによって異なります.
タイタンの魅力の鍵は,酸素にさらされたときにセラミックのような酸化膜が自然に形成され,特殊な腐食と侵食耐性を与えることです.この 自治する 酸化物 の 層 は,酸素 に 接触 する 時 の 傷 を 軽減 する.
生物相容性があるチタンは 医療用インプラントに広く使われています 膝や腰の義肢 ペースメーカーのケース 歯科インプラントや頭蓋骨のプレートなどです高温で強度を維持する能力高度な溶融点,優れた強度/重量比,様々な酸化環境 (塩水や塩水を含む) の腐食耐性低弾性モジュールは,さらにその多様性を強調します.
結論として タイタンの耐久性,弾力性,適応性の組み合わせは 様々な産業における 重要な材料としての地位を 強化しています未来における継続的なイノベーションと応用を約束する.